Exchange Active Policies help you to remotely configure Android, iPhone and Windows Phone smartphones and Exchange Remote Wipe allows you to remotely erase all data on a lost smartphone.
Since the uptake of smartphones has become more widespread, it is more than likely that your end users will require access to their corporate email via their smartphones. Whether or not the smartphone is company supplied . It is certainly a sensible idea to make sure that we have policies in place to protect our data should it end up in the wrong hands.

Once a compatible ActiveSync device is synchronized with your Exchange organization, the appropriate policy will be applied, and the smartphone will react accordingly. It should be noted though that these policies do not apply to all devices , so it’s important to check it out first. The vast majority of smartphones in our organization are iPhones – Apple published a list of the supported policies on their developer site.
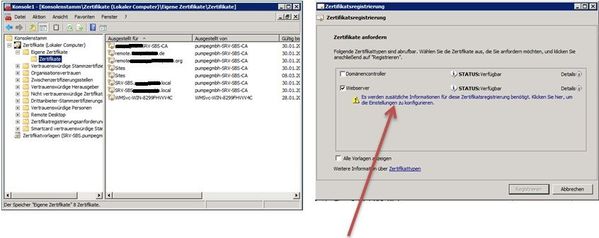
Chances are that the end users will just ring the helpdesk to request that the device be remotely wiped. An Exchange administrator can easily do this from the Exchange Management Console. Navigate to the Recipient Configuration\Mailbox node from the tree view. In the main area of the console, right click the user in question, then select “manage mobile phone” from the context menu. You will be presented with a list of mobile devices that are associated with the user’s Exchange account – select the appropriate device, click the “remote wipe” radio button, then click the “clear” button.

Since the uptake of smartphones has become more widespread, it is more than likely that your end users will require access to their corporate email via their smartphones. Whether or not the smartphone is company supplied . It is certainly a sensible idea to make sure that we have policies in place to protect our data should it end up in the wrong hands.
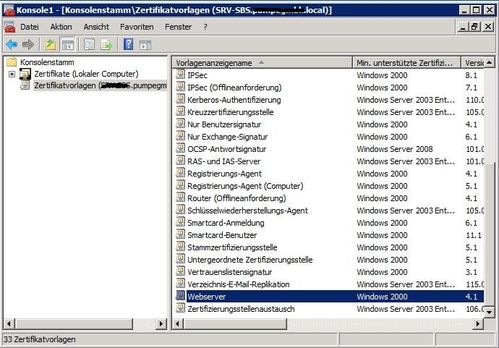
Exchange ActiveSync Mailbox Policies
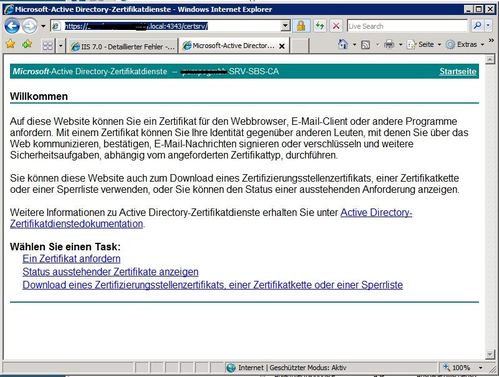
Exchange 2010 has a feature called “Exchange ActiveSync Mailbox Policies”. You can find this in the Exchange Management Console, within the “Organization Configuration\Client Access” node from the tree view. You will notice that within the Exchange ActiveSync Mailbox Policies tab, you can create multiple policies – these can then be applied to different groups of users. I just want a common policy throughout my entire organization, so I will just modify the default policy that is already listed.
Exchange ActiveSync Mailbox Policies
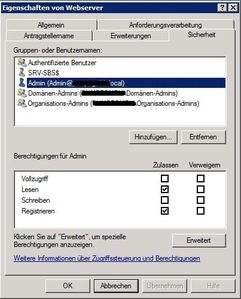
Using the policy properties, you can force devices to use a passcode, set the minimum length or enable encryption, and so on.We can disable some function of an smartphone such as its camera, or Wi-Fi should this be a requirement in your organization.Once a compatible ActiveSync device is synchronized with your Exchange organization, the appropriate policy will be applied, and the smartphone will react accordingly. It should be noted though that these policies do not apply to all devices , so it’s important to check it out first. The vast majority of smartphones in our organization are iPhones – Apple published a list of the supported policies on their developer site.
Exchange Remote Wipe
Should the inevitable happen, and a user loses their phone with all their company emails and trade secrets on it, and it doesn’t look like it’s coming back any time soon, we have a couple of ways of performing a remote device wipe. Firstly, the end user can do it on their own via Outlook Web Access (great if they lose the device when the helpdesk isn’t yet open!). The user will need to log into OWA, and select options from the top right, then select “see all options” from the menu. Once you’re in the OWA options screen, select phone from the right, and you should be presented with a list of mobile devices associated with your Exchange account. From the list of devices, simply select the device in question, and click the “wipe device button”.Chances are that the end users will just ring the helpdesk to request that the device be remotely wiped. An Exchange administrator can easily do this from the Exchange Management Console. Navigate to the Recipient Configuration\Mailbox node from the tree view. In the main area of the console, right click the user in question, then select “manage mobile phone” from the context menu. You will be presented with a list of mobile devices that are associated with the user’s Exchange account – select the appropriate device, click the “remote wipe” radio button, then click the “clear” button.

Exchange Remote Wipe
Shortly after this, the mobile device should perform a full wipe and erase all data. If your staff are accessing your corporate emails via their personal smartphones, it might be an idea to let them know that you have the ability to wipe mobile devices should they be lost – many users might lose their smartphones and never tell you otherwise!