Access to corporate resources from external computers requires secure authentication methods. This article explains how to configure One-Time Password pre-authentication.
In the previous article of this Kerberos Delegation series, you learned how to configure Kerberos Constrained Delegation. Today, I will discuss pre-authentication methods that are not based on Active Directory. Users can pre-authenticate using Windows Active Directory authentication, RADIUS OTP authentication, Certificate authentication or LDAP authentication, and even with PKI certificates.
In the example here, we will use a one-time password solution that provides a simple, user friendly and very secure solution that is ideal for securing access to corporate resources when used with Microsoft (TMG) and Kerberos Constrained Delegation. I will describe how Protocol Transition works with TMG, i.e. how you can authenticate users with one method and then pass the credentials to the backend using Kerberos.
So how is the end-user experience when multiple pre-authentication methods are used without Credential Delegation? If you were to use RADIUS One-Time Password pre-authentication on the TMG Listener, a user would have to enter his OTP credentials first and then provide his Windows credentials for access to the web server.
Why is this not good? You expose critical security information (Domain username and password, which are static) when a user has to enter Domain credentials on a machine that doesn’t belong to your corporate network. This is especially problematic in a “hostile” environment such as internet cafes or the “mother-in-law” computer (I heard this term at a Microsoft presentation for UAG and I just had to use it). You can probably imagine the variety of threats in those environments. Such a machine could run key logging malware that collects static passwords and other information that could be used in a subsequent attack.
How can a security minded administrator make sure that users would enter only OTP credentials when accessing backend HTTP/HTTPS based services? It’s obvious that you can’t achieve this by using Basic Credential Delegation which means passing username and password from the TMG server to the backend server. For working with OTP credentials, Kerberos Constrained Delegation and Protocol Transition is required.
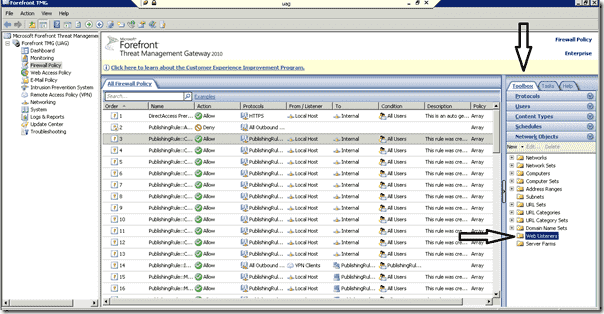
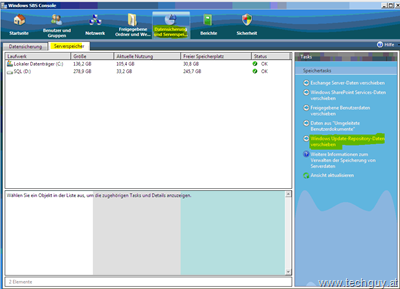
In my previous article, I already explained how to configure Kerberos Constrained Delegation in a Publishing rule. In this post, I will describe how to configure the Listener to use OTP and PKI pre-authentication. But first we have to configure TMG to query an authentication server. We will do this by defining a RADIUS server with TMG. First select “Tasks” in the TMG console.
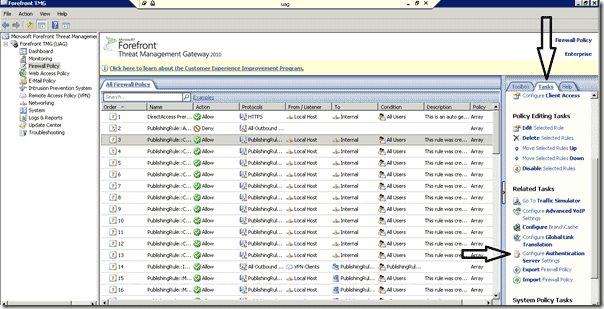
TMG – Configure Authentication
Locate “Configure Authentication Server settings”
A new window will pop up, click “add” and enter the relevant information (IP, Shared Secret And Port). Also be aware, that if your RADIUS server uses a port other than 1812, you will have to allow it independently.
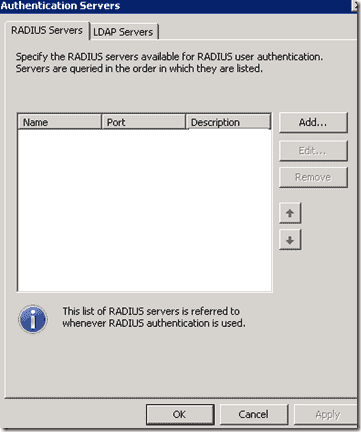
TMG – Authentication Servers
I continue by reconfiguring the Listener on the TMG from the previous article. Select “Toolbox” and then click on “Network Objects” in the TMG Console.
TMG – Web Listeners
Locate and open the “Web Listener” dialog at the bottom and right click the Listener that you created in the previous article.
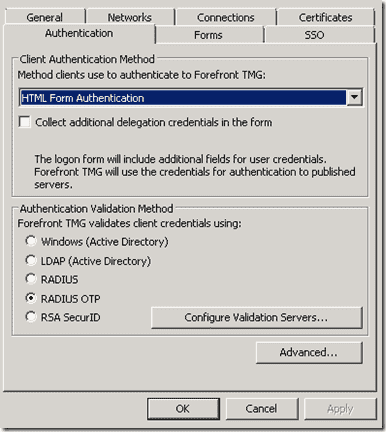
Authentication Validation Method
Now select “RADIUS OTP” authentication in the Authentication settings tab. You can then use this Listener in a Publishing Rule. The Publishing Rule from the previous article can be used without reconfiguration. Click OK and Apply.
How would an end user experience this? When a user first accesses the URL of the published web application, he will be asked to enter his OTP credentials. The TMG would then authenticate him to the backend application using a Kerberos Token by delegating the credentials. The user has successfully logged in using only his OTP credentials without being asked to enter his domain credentials. In the next article, I will explain how to use Smart Cards and PKI credentials to access published resources.